You’d see more and more electric cars on the streets lately as they’re quickly becoming a normal part of everyday life.
These cars represent a big step forward in how we think about transportation. People are drawn to them because they’re modern, efficient, and often quieter than regular cars.
Around the world, car companies are focusing on building electric models that fit different needs and lifestyles.
Governments and car companies are also supporting electric cars by building more charging stations and offering rebates. As this change continues, electric cars are changing the future of travel.
What are Electric Cars?
Electric vehicles are machines that use electricity instead of gasoline to move. Among them, electric cars are the most common and widely used today.
These cars run on power stored in large batteries rather than burning fuel in an engine. The battery sends energy to a motor that helps the car move smoothly and quietly.
Since electric cars don’t use gasoline, they don’t produce exhaust or harmful gases, making them better for the environment.
They are also designed to be efficient, with fewer moving parts than regular cars, which means they often need less maintenance.
As technology improves, electric cars continue to grow in popularity and performance around the world.
What are the Types of Electric Cars?
There are several kinds of electric cars, and each one uses electricity in its own way. Understanding the different types helps drivers choose the one that fits their lifestyle and travel needs.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): These cars run only on electricity stored in large batteries. They need to be plugged in to recharge and do not use gasoline at all.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These have both an electric battery and a gasoline engine. When the battery runs low, the car automatically switches to gas power, making it great for longer drives.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): These can’t be plugged in. Instead, the battery recharges while driving, using energy from the gasoline engine and braking.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): These cars use hydrogen to make electricity inside the vehicle. They emit only water vapor, making them one of the cleanest types of electric cars available.
How do Electric Cars Work?


Image Source: Hyundai USA
Electric cars work by using electricity instead of gasoline to make the vehicle move.
The main power source is a large battery that stores electrical energy. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the battery sends this energy through a device called a controller.
The controller manages how much electricity flows to the motor, depending on how fast the driver wants to go.
The electric motor then changes the electrical energy into motion, turning the wheels and moving the car forward. Since electric cars don’t have engines or complex gear systems, the process is quiet and smooth.
When the car slows down, some systems can even capture energy and send it back to the battery for later use.
This simple and efficient setup makes electric cars reliable, responsive, and well-suited for everyday travel.
Components of Electric Cars
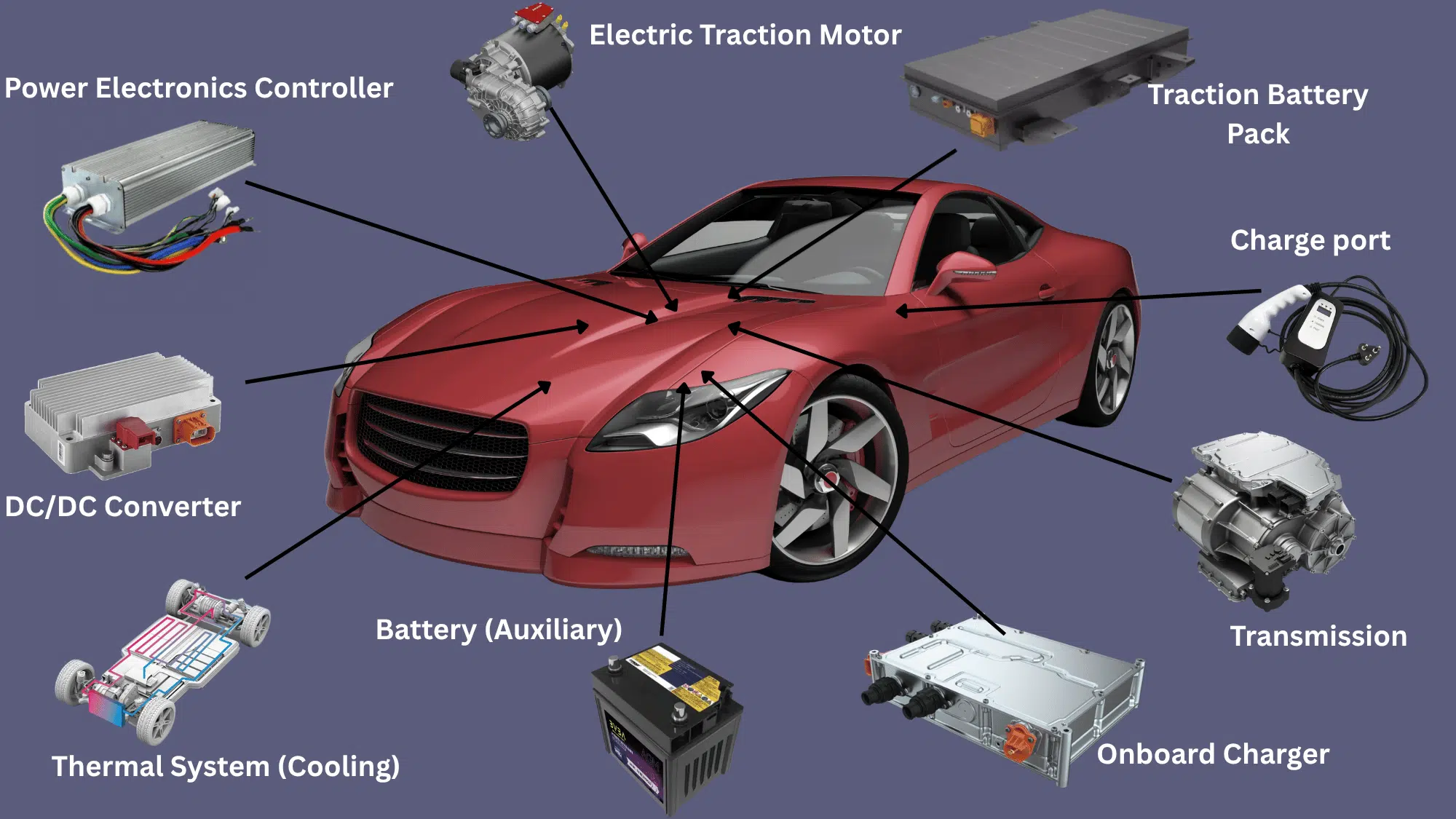

To understand how electric cars work, it is also important to know their components. Each component has a specific job, and all of them must function smoothly for the car to perform well on the road.
Battery (All-Electric Auxiliary)
The all-electric auxiliary battery provides power for smaller systems in the car, such as lights, dashboard displays, and safety features.
It works alongside the main traction battery pack but handles lower-voltage functions. This battery ensures that electrical parts stay active even when the main system is off.
It helps start the vehicle’s control systems and supports comfort and safety equipment during operation.
Charge Port
The charge port is the connection point where electricity enters the car.
It allows the vehicle to plug into an external power source, such as a home outlet or public charging station. The port directs electricity safely to the onboard charger.
Different cars may use different plug types, but all charge ports are designed to handle high power levels and protect against overheating during charging.
DC/DC Converter
The DC/DC converter takes the high-voltage electricity from the main battery and changes it into lower-voltage power for other systems in the car.
This allows smaller devices like lights, sensors, and control modules to work properly. It keeps the voltage steady and prevents electrical damage.
The converter is an important part of managing energy safely across all parts of the vehicle.
Electric Traction Motor
The electric traction motor turns electrical energy into motion. It creates spinning power that moves the wheels and allows the car to accelerate smoothly.
When the car slows down, the motor can also reverse its role to recover energy and send it back to the battery.
Electric motors are known for being quiet, efficient, and quick to respond to the driver’s input.
Onboard Charger
The onboard charger manages the flow of electricity from the charging station to the battery.
It converts alternating current (AC) from the power source into direct current (DC) for storage in the battery pack. The charger also controls the charging speed and prevents overcharging.
It plays an important role in maintaining battery health and ensuring safe and efficient charging every time.
Power Electronics Controller
The power electronics controller manages how energy moves between the battery and the traction motor.
It controls speed, torque, and power delivery based on signals from the accelerator pedal. Adjusting voltage and current helps the car run smoothly at different speeds.
This component ensures that the motor gets the right amount of power for both acceleration and energy recovery.
Thermal System (Cooling)
The thermal system keeps the electric car’s components at safe temperatures.
It cools the battery, motor, and power electronics when they get too warm during driving or charging. It may use liquid or air cooling to move heat away from sensitive parts.
Proper temperature control helps prevent overheating, improves efficiency, and extends the life of key electrical systems.
Traction Battery Pack
The traction battery pack stores the main supply of electrical energy that powers the car.
It is made up of many small cells linked together to create high voltage. The amount of energy it holds determines how far the car can travel before recharging.
The pack is built for durability, with protective housing to guard against impact, temperature changes, and moisture.
Transmission (Electric)
The electric transmission transfers power from the traction motor to the wheels.
Unlike a gas car’s multi-gear system, most electric transmissions use a single gear to deliver power efficiently. This design allows for smooth acceleration without gear shifting.
It also helps reduce mechanical wear and energy loss. The transmission’s simplicity improves reliability and supports a quiet, steady driving experience.
How to Charge Electric Cars?
Charging an electric car is simple and can be done at home or at public stations. The time it takes to charge depends on the type of charger being used, and each level provides different speeds and power.
- Level 1 charging: This uses a standard home outlet and provides the slowest charging speed. It’s best for overnight charging or short daily commutes since it adds only a few miles of range per hour.
- Level 2 charging: This option uses a special charging unit found at homes or public stations. It delivers more power than level 1 and can fully charge most cars in several hours, making it ideal for regular use.
- Fast charging: Also called dc fast charging, this is available at special stations and can charge a battery up to 80% in less than an hour.
The type of charger you use affects how quickly the battery fills and how convenient charging is for daily driving. Drivers can easily locate charging stations using apps or online maps that show available spots nearby.
Pros and Cons of Electric Cars
Electric cars have many good points, but they also come with a few limits. Knowing both helps drivers understand what to expect before switching from gasoline to electric.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower fuel costs because they use electricity instead of gasoline. | Higher upfront cost compared to similar gas cars. |
| Smooth acceleration and steady performance at all speeds. | Charging can take several hours, depending on the charger type. |
| Fewer mechanical parts, which reduces the chance of breakdowns. | Battery performance can decrease in very hot or cold weather. |
| Quieter operation, reducing noise in busy areas. | Some areas have limited access to public charging stations. |
| It can be powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind. | Battery replacement can be expensive after several years. |
Conclusion
Electric cars are an important part of the future of transportation. They show how technology can make travel cleaner, smarter, and more efficient.
As research continues, batteries are becoming lighter, stronger, and faster to charge.
Car companies are also improving designs to make electric models more affordable and practical for everyday use.
Governments and cities are supporting this shift by adding more charging stations and offering incentives to buyers.
With these changes, electric cars are moving from a new idea to a normal choice for many people who want a reliable and environmentally friendly way to get around.

