Electric vehicles are changing the way we travel, offering cleaner and smarter transportation. As more people switch to EVs, charging methods are also becoming more advanced.
One exciting improvement is wireless charging, which makes powering up cars easier than ever.
It’s designed to save time, reduce clutter, and make charging as simple as parking your car.
This new approach could reshape how we think about energy and convenience in the future.
This blog will explain how wireless charging works for electric vehicles, the science behind it, and what makes it an important step toward a more connected world.
What is Wireless Charging Technology?
Wireless charging technology is a modern way to power electric vehicles without the need for plugs or cables.
Instead of connecting a charger by hand, the car uses special parts built into the ground and the vehicle to receive energy.
When the car is parked in the right place, the system starts charging automatically. This makes the process simple, clean, and easy to use.
Drivers don’t have to deal with tangled cords or worry about bad weather. Many car makers and cities are testing this technology to make charging stations more convenient.
It’s part of a bigger move toward smart transportation that saves time, reduces effort, and supports a cleaner, energy-efficient future for everyone.
Types of Wireless Charging for Electric Vehicles
Wireless charging for electric vehicles comes in a few different forms. Each type helps make charging easier and more flexible for drivers.
- Static Charging: This type lets the car charge while it is parked over a charging pad on the ground. It’s easy to use and works well for homes, offices, or public parking areas.
- Dynamic Charging: In this system, the car charges while driving on roads that have special power lines built underneath. It helps drivers travel longer distances without stopping to recharge.
- Stationary Pad Systems: These charging pads are placed in fixed spots like malls, bus stops, or workplaces. They make it simple for drivers to charge their cars during short stops or daily routines.
How Does Wireless Charging Work for Electric Vehicles?
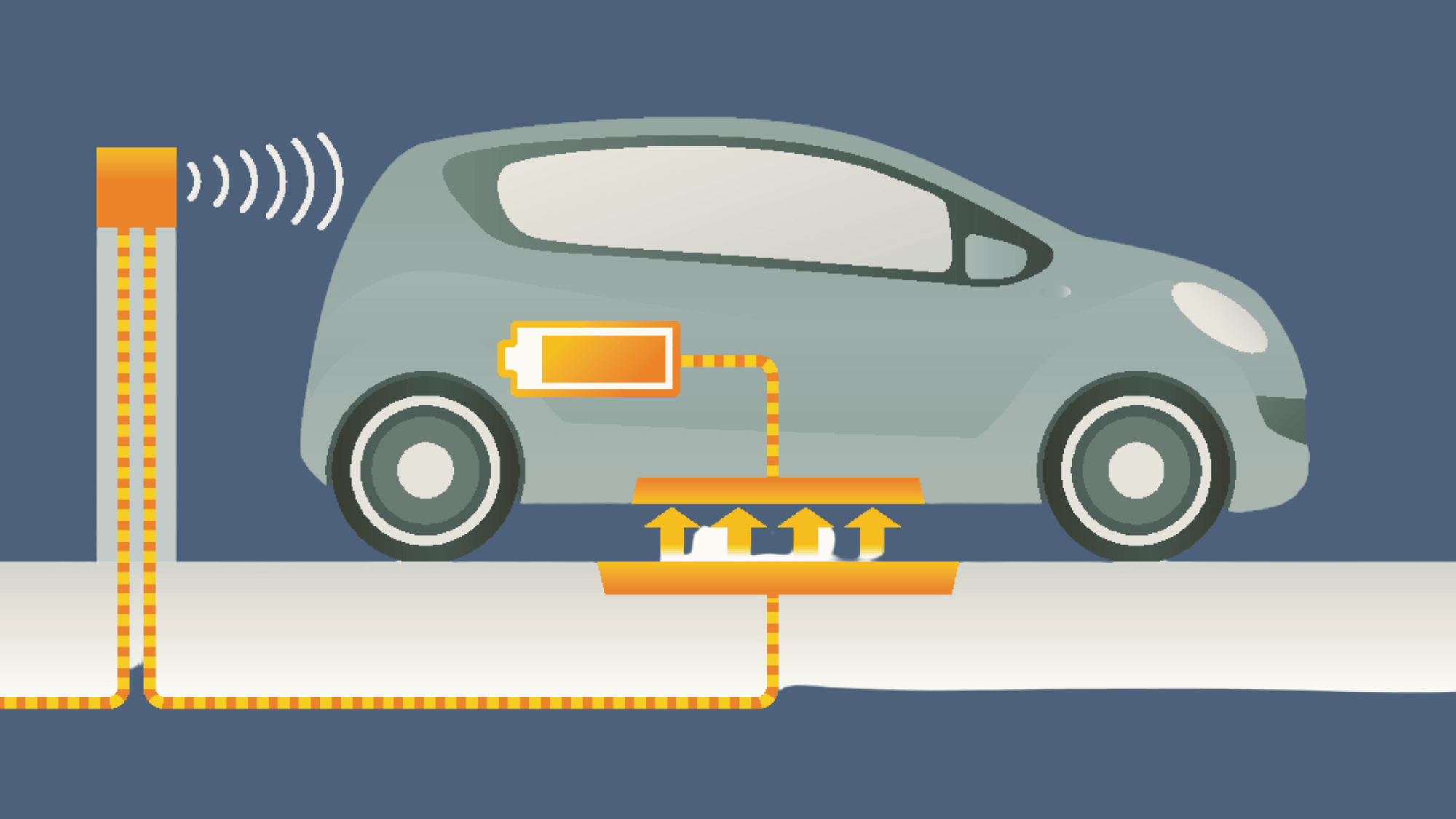

Wireless charging for electric vehicles uses two main parts that work together to send power safely.
The ground pad, or transmitter, is placed on or under the parking area and creates a magnetic field that carries energy.
The receiver pad, attached to the bottom of the car, collects this energy and delivers it to the battery for storage.
Here’s how it works step by step:
- Park the Car: The driver parks the car directly over the ground pad. The system checks if the car is in the right position before charging begins.
- Send the Energy: The ground pad creates magnetic waves that carry power through the air to the car. This happens safely without any wires or sparks.
- Convert the Energy: The receiver pad changes the magnetic energy into electric power the battery can use. The process is smooth and automatic.
- Store the Charge: The converted electricity moves into the car’s battery and gets stored. Once full, the system stops charging on its own to save energy.
Principles of Wireless Charging Technology
Wireless charging technology is based on a few simple scientific ideas that make it safe and efficient.
The main principle is called magnetic induction, which happens when electricity in one coil creates a magnetic field. This invisible field can pass energy to another coil nearby without any direct contact.
In electric vehicles, the first coil is inside the charging pad on the ground, and the second coil is in the car’s receiver.
When they are close together, the energy moves from the pad to the car, where it is turned into electricity that charges the battery.
Another important idea is resonance, which helps the energy move more easily between the coils, even if they are a little farther apart.
Installation and Safety Standards for Wireless Charging Technology


Installing a wireless charging system for electric vehicles requires careful setup to make sure it works safely and efficiently.
The ground pad must be placed on a flat surface and aligned correctly with the car’s receiver pad so the energy can transfer smoothly.
Even a small gap or misalignment can reduce charging speed, so many systems include sensors or lights to help guide parking.
Electrical safety is also very important. The equipment is built with shielding to keep magnetic fields contained and prevent interference with other electronics.
There are also global standards, such as those from the SAE and ISO, that set rules for safety, compatibility, and performance.
Pros and Cons of Wireless Charging Technology
Wireless charging for electric vehicles offers many benefits, but it also has a few challenges. Understanding both can help drivers decide if it’s the right choice for their needs.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to Use: Just park the car, and charging starts automatically. | Higher Cost: Installation and equipment can be more expensive than plug-in chargers. |
| Safe in Any Weather: No cables or plugs mean less risk in rain or snow. | Slower Charging Speed: It can take longer to charge compared to traditional plug-in systems. |
| Less Wear and Tear: No need to handle cords, which keeps parts in better shape. | Needs Perfect Alignment: The car must be parked exactly over the pad for best results. |
| Cleaner Setup: No messy cords or cables make it neat and simple. | Limited Availability: Still not common in most public places or homes. |
The Future of EV Wireless Charging
The future of wireless charging for electric vehicles looks bright as more companies and cities begin testing the technology.
Several automakers, including BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Hyundai, are developing cars that can charge wirelessly at home or in public spaces.
In Norway, Germany, and the United States, pilot programs are building dynamic charging roads that let EVs charge while driving. For example, a test road in Detroit powers cars as they move using coils buried under the surface.
Experts believe that within the next five to ten years, wireless charging pads could become common in parking lots, taxi stands, and even highways.
As the technology improves, charging efficiency is expected to reach 90% or higher, making it almost as effective as plug-in systems.
Conclusion
Wireless charging is becoming an important part of the future of electric vehicles.
It offers a simple, hands-free way to power cars without plugs or cables. As technology improves, charging will become faster, safer, and more efficient.
Many cities and car makers are already testing systems that could make charging pads common in public places and homes.
This innovation will make owning an electric car easier and more convenient for everyone.
With continued progress, wireless charging could help create cleaner roads, reduce dependence on fuel, and make electric travel a normal part of everyday life.

