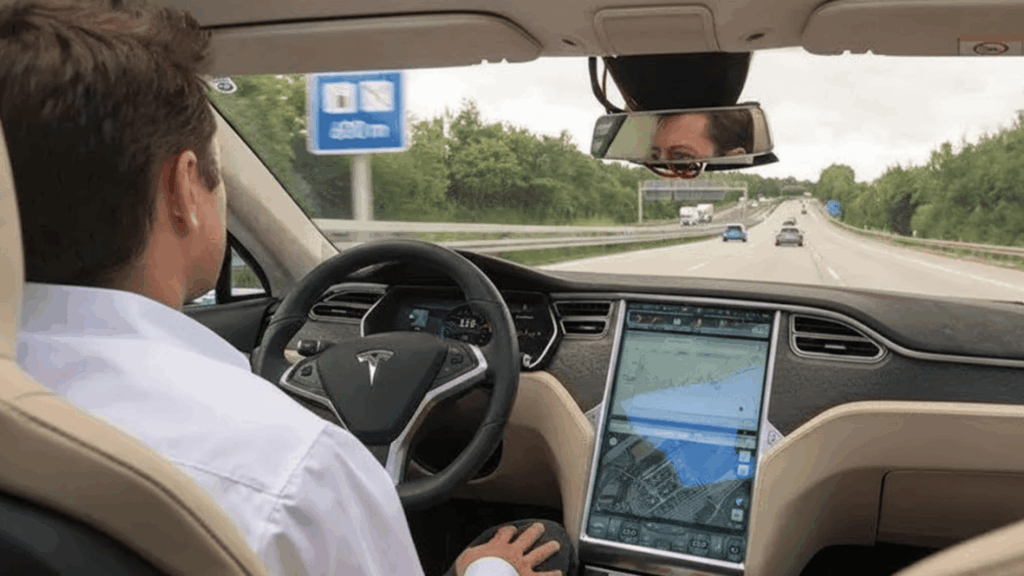
I’ve always been impressed by how cars are getting smarter every year. The idea of self-driving cars sounds like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, but it’s already becoming real.
Some people think these cars will make roads safer and life easier, while others worry about safety and job loss.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through the pros and cons of self-driving cars, how they actually work, and what this new technology could mean for society and the economy.
By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of both the benefits and the challenges that come with autonomous vehicles, and where the future of transportation might be headed.
What Are Self-Driving Cars?
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, are vehicles equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence that allow them to navigate without direct human control.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines six levels of automation, ranging from manual driving to fully autonomous systems. Each level represents how much the car controls versus the driver.
Levels of Automation:
- Level 0: No automation; driver handles everything.
- Level 1–2: Basic assistance like cruise control or lane-keeping.
- Level 3–4: Conditional automation under specific conditions.
- Level 5: Fully autonomous; no human needed.
In short, true self-driving cars operate entirely on their own, without any human intervention or steering wheel input.
How Do Self-Driving Cars Work?
Self-driving cars, or autonomous vehicles, operate using a combination of sensors, artificial intelligence, and real-time data.
These systems constantly monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, interpret traffic conditions, and make instant decisions to ensure safe navigation without human control.
Here’s a breakdown of the core technologies that make this possible.
| Technology | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensors (LiDAR, Radar, Cameras) | Detect objects, pedestrians, lane markings, and other vehicles in the environment. |
| AI Algorithms & Machine Learning | Analyze sensor data, predict movements, and decide how the car should respond. |
| On-board Computers & Actuators | Convert AI decisions into real actions like steering, braking, and accelerating. |
| GPS & Real-Time Mapping | Help the car understand its position, follow routes, and adapt to changing conditions. |
Despite their precision, autonomous driving systems face challenges such as poor weather, obscured lane markings, and unexpected road conditions.
These factors can reduce visibility or sensor accuracy, sometimes requiring human intervention.
So, self-driving cars work by combining advanced sensing, intelligent computing, and continuous data integration to drive safely and efficiently.
Pros and Cons of Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars are changing the way people think about transportation, bringing exciting advantages and serious challenges that will shape the future of mobility and everyday travel.
Pros of Self-Driving Cars
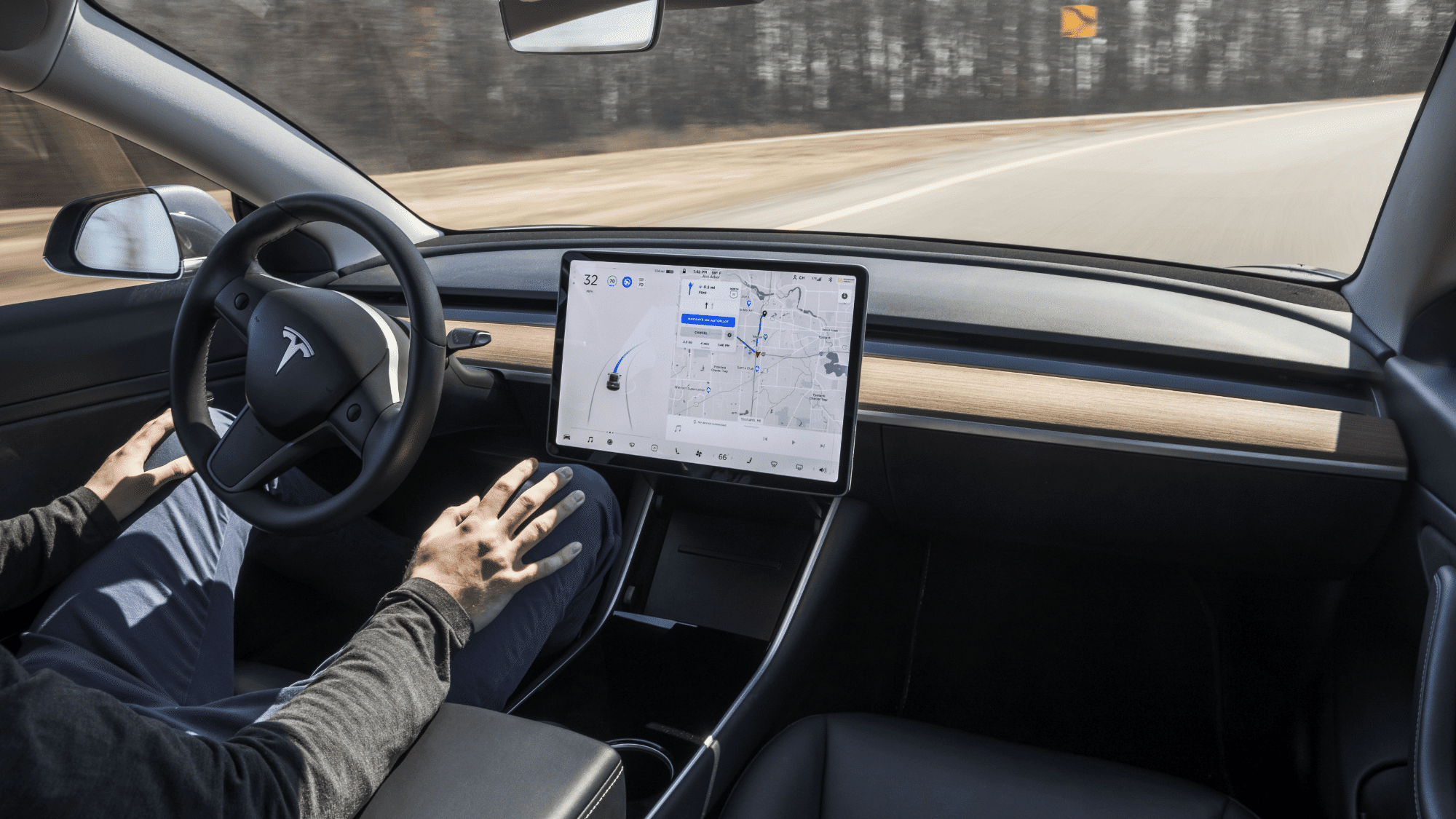

While the technology is still developing, autonomous vehicles already offer several promising benefits that make driving safer, greener, and more efficient for both individuals and businesses.
1. Improved Road Safety
One of the biggest advantages of self-driving cars is their ability to drastically cut down on accidents caused by human error.
These cars don’t get distracted, tired, or emotional. Their built-in systems react faster than people ever could, making roads safer for everyone.
- Reduces crash risks and fatalities.
- Reacts instantly to road hazards.
- Eliminates drunk or distracted driving.
2. Greater Accessibility
For those who can’t drive because of age, disability, or medical conditions, autonomous vehicles could be life-changing.
They make travel easy and convenient with hands-free navigation and voice controls, opening doors to independence and freedom like never before.
- Helps elderly and disabled individuals stay mobile.
- Expands access to transportation options.
- Encourages independence and confidence.
3. Reduced Traffic Congestion
Traffic jams could soon be a thing of the past with self-driving technology. These cars can communicate with one another to maintain smooth traffic flow, adjust speeds automatically, and minimize stop-and-go driving that wastes time and fuel.
- Uses smart routing to avoid congestion.
- Reduces idle time and fuel use.
- Improves travel times on busy routes.
4. Environmental Efficiency
Self-driving cars are built to drive smartly, not aggressively. They accelerate and brake smoothly, cutting down on fuel consumption and emissions.
Pairing them with electric vehicle technology could make transportation cleaner and greener than ever.
- Lowers overall emissions.
- Improves fuel and energy efficiency.
- Supports global sustainability goals.
5. Economic Benefits
For businesses, autonomous vehicles are a dream come true. They can run nonstop, deliver goods efficiently, and reduce labor costs. Plus, fewer accidents mean lower insurance rates and maintenance expenses over time.
- Boosts productivity and efficiency.
- Cuts operating and labor costs.
- Saves money through fewer accidents and repairs.
Cons of Self-Driving Cars
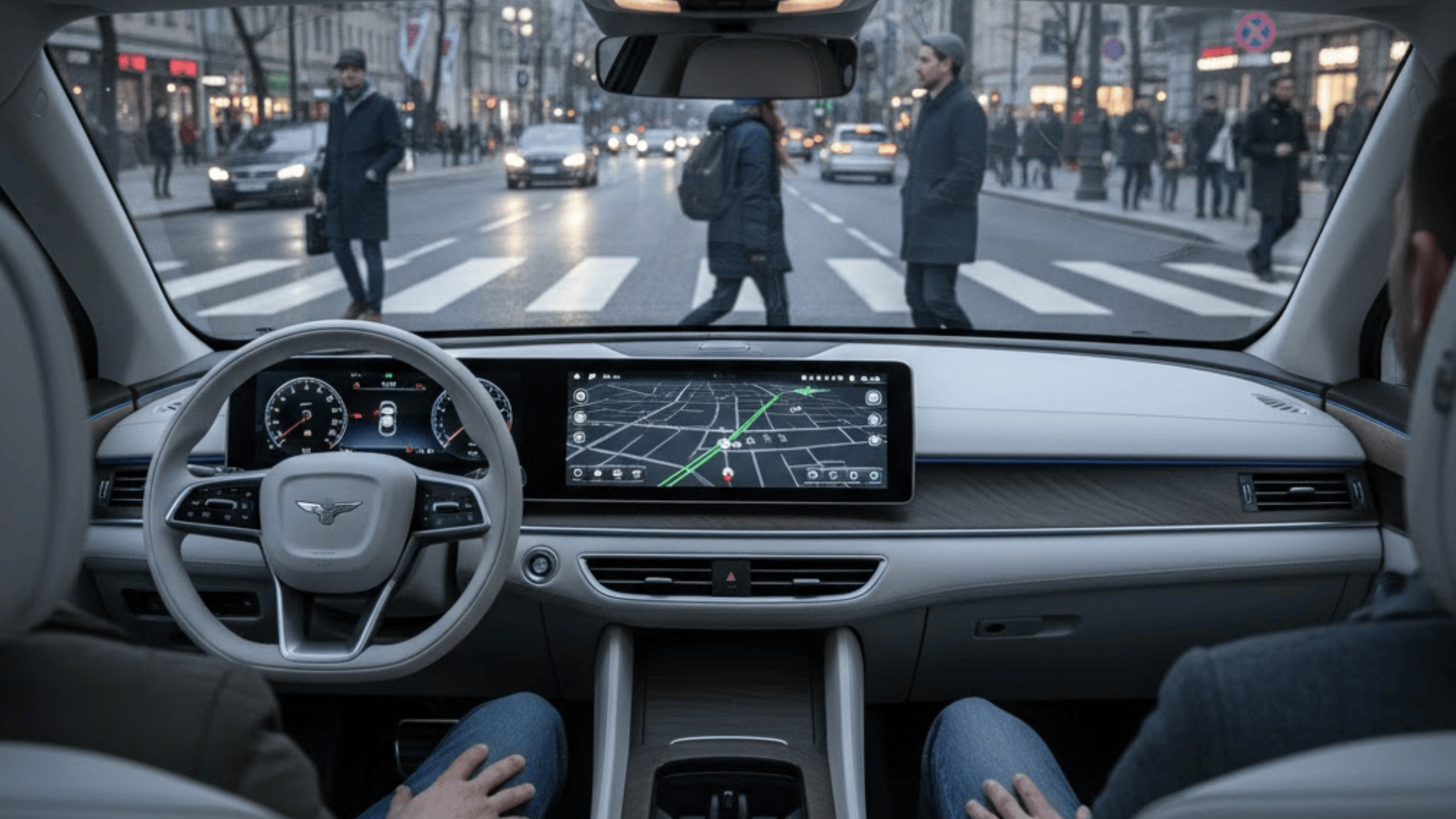

While self-driving cars promise innovation and convenience, they also come with serious challenges that affect safety, cost, employment, and how people adapt to this new technology.
1. Safety and Reliability Concerns
Even with advanced sensors and algorithms, self-driving cars aren’t perfect. They can struggle in unpredictable real-world situations like sudden lane changes or jaywalking pedestrians.
Technical malfunctions or software glitches could lead to serious accidents, raising big questions about trust and reliability.
- Prone to technical or sensor errors.
- Can misread complex traffic scenarios.
- Still needs human supervision in many cases.
2. High Costs
Owning or developing a fully autonomous vehicle doesn’t come cheap. The technology involves expensive components like LiDAR sensors, AI processors, and specialized cameras.
Until production becomes more affordable, self-driving cars will likely remain out of reach for the average consumer.
- High manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Expensive software updates and repairs.
- Limited affordability for most buyers.
3. Job Displacement
The rise of automation in transportation could mean fewer jobs for human drivers. Truckers, taxi operators, and delivery personnel might find their roles replaced by machines, creating major economic and social challenges.
- Reduces employment in driving industries.
- Forces large-scale job retraining.
- Disrupts traditional livelihoods.
4. Ethical and Legal Dilemmas
When accidents happen, who’s responsible: the passenger, the manufacturer, or the software? Autonomous vehicles also face moral questions in unavoidable crash situations.
These ethical and legal challenges make it difficult to regulate self-driving cars effectively.
- Unclear legal accountability.
- No moral judgment in emergencies.
- Creates regulatory confusion.
5. Weather and Infrastructure Challenges
Bad weather can easily interfere with how autonomous vehicles operate. Heavy rain, fog, or snow can block sensors, while faded lane markings or poor roads can confuse navigation systems.
These conditions limit the reliability of self-driving cars in many areas.
- Sensors struggle in poor visibility.
- Needs strong infrastructure support.
- Performs best in ideal conditions only.
Impact on Society and the Economy of Self-Driving Cars
The rise of self-driving cars is set to transform not just transportation but the entire way people live, work, and move through cities.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic Transformation | Logistics, delivery, and ride-hailing services could become cheaper and faster, while industries like insurance, auto repair, and fuel may need to reinvent their business models. |
| Urban Design | With fewer parking needs, cities can reclaim space for housing, parks, or walkable areas, reshaping urban planning for cleaner, less congested environments. |
| Human Behavior | People may move away from traditional car ownership toward ride-sharing or subscription models, changing how commuting and travel fit into daily life. |
| Social Concerns | Self-driving technology could deepen the digital divide if access is limited to wealthier groups. Data collection also raises concerns about privacy and tracking. |
Ultimately, the impact of self-driving cars on society will depend on how fairly technology is implemented and how quickly regulations adapt to balance innovation with equity.
Who’s Leading the Autonomous Vehicle Market?
The race to perfect self-driving technology is heating up, with major automakers and tech innovators taking big strides toward autonomy.
Each company brings a unique approach, whether focused on urban ride-hailing, long-haul trucking, or hands-free highway driving. Here’s a closer look at the key players steering the future.
1. Waymo
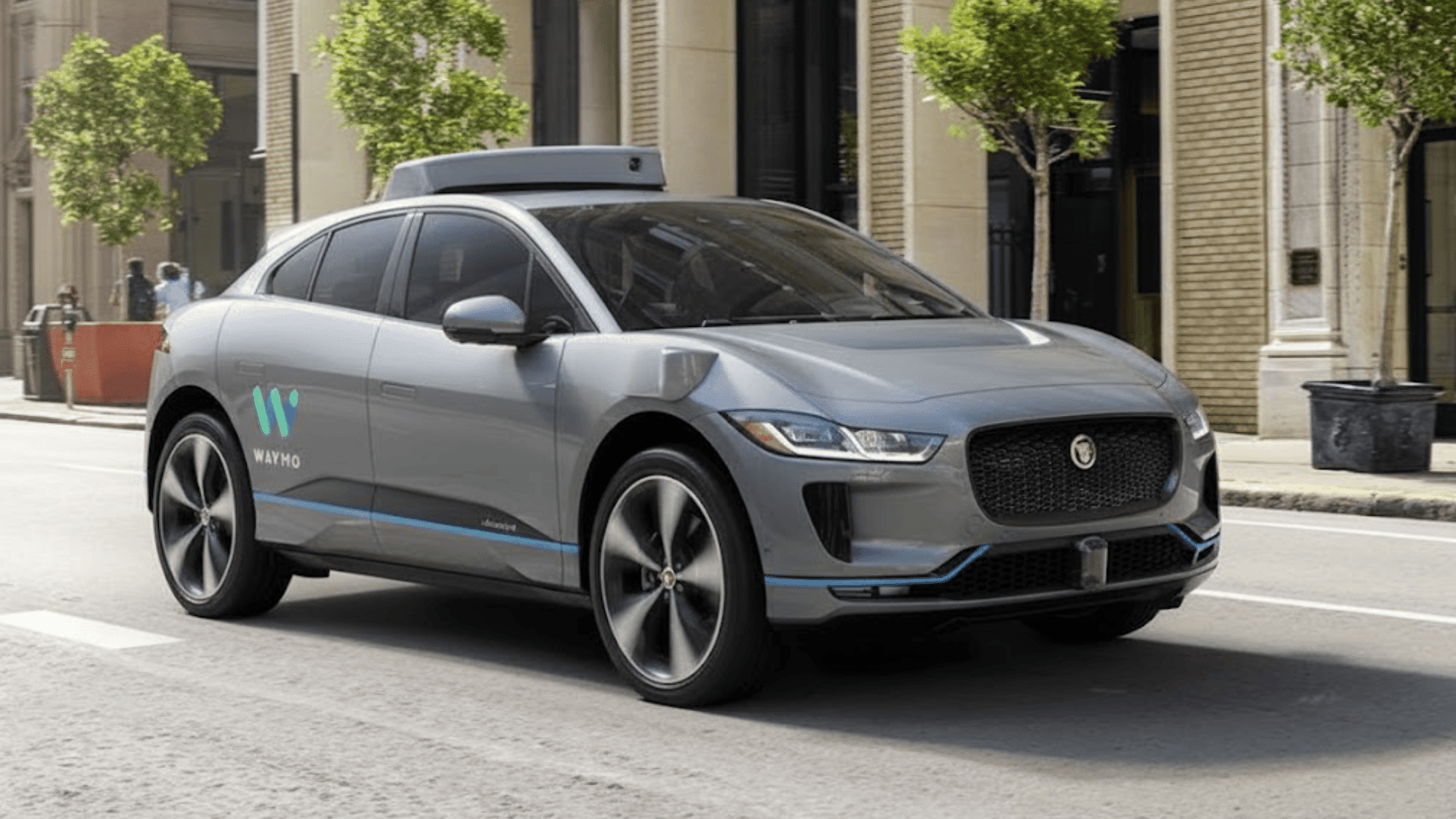


Waymo, backed by Google’s parent company Alphabet, stands out as a pioneer in autonomous driving. Its robotaxi services operate in cities like San Francisco, Phoenix, Austin, and Los Angeles, offering rides with no human behind the wheel.
- Testing Level 4 autonomy in multiple U.S. cities.
- Specializes in urban ride-hailing.
- Expanding coverage across new markets.
2. Tesla


Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) system has become one of the most well-known names in the self-driving space. While it’s still classified as Level 2 automation, its software continues to evolve through regular updates that push the boundaries of what’s possible.
- Uses camera-based vision instead of LiDAR.
- Works globally on public roads.
- Constantly improving through data collection.
3. Cruise


Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, is making strong progress with its driverless taxis. Operating mainly in San Francisco and Phoenix, Cruise aims to make autonomous ride-hailing a reality, though it’s still refining safety and regulatory compliance.
- Focused on Level 4 autonomous driving.
- Supported by GM and Honda.
- Testing in complex city traffic environments.
4. Ford BlueCruise


BlueCruise from Ford delivers hands-free driving on mapped highways across North America. It’s not fully autonomous yet; it’s a Level 2 system, but it’s a major step toward safe, convenient semi-autonomous travel.
- Covers over 400,000 miles of mapped routes.
- Subscription-based system for flexibility.
- Designed for comfortable long-distance drives.
5. GM Super Cruise
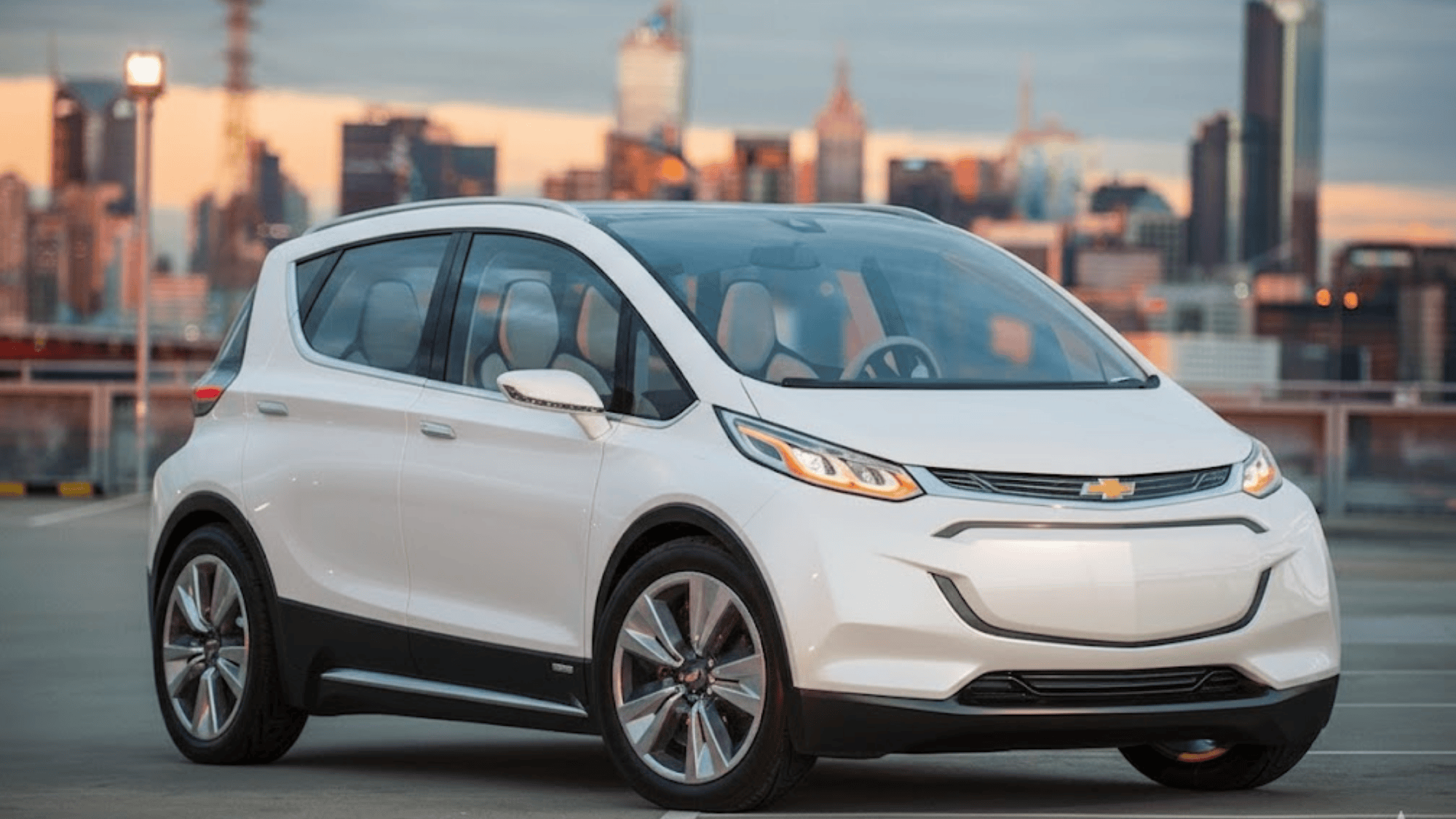

GM’s Super Cruise is another standout in the semi-autonomous segment. It offers hands-free driving under specific conditions, mainly on highways, giving everyday drivers a taste of future mobility.
- Level 2 automation with LiDAR mapping.
- Includes real-time driver monitoring.
- Available on Cadillac, Chevrolet, and GMC vehicles.
6. Gatik


Gatik focuses on making delivery logistics more efficient with autonomous box trucks that handle short, repeatable routes between warehouses and stores. This targeted approach allows for faster, safer automation.
- Operates Level 4 autonomous trucks.
- Partners include Walmart and Kroger.
- Runs mainly in Texas and Arkansas.
7. Kodiak Robotics


Kodiak Robotics is transforming long-haul trucking by integrating self-driving systems into semi-trucks. With an emphasis on reliability and safety, these trucks aim to keep freight moving smoothly around the clock.
- Specializes in autonomous freight logistics.
- Currently includes safety drivers during tests.
- Operating routes across the southern U.S.
8. Einride
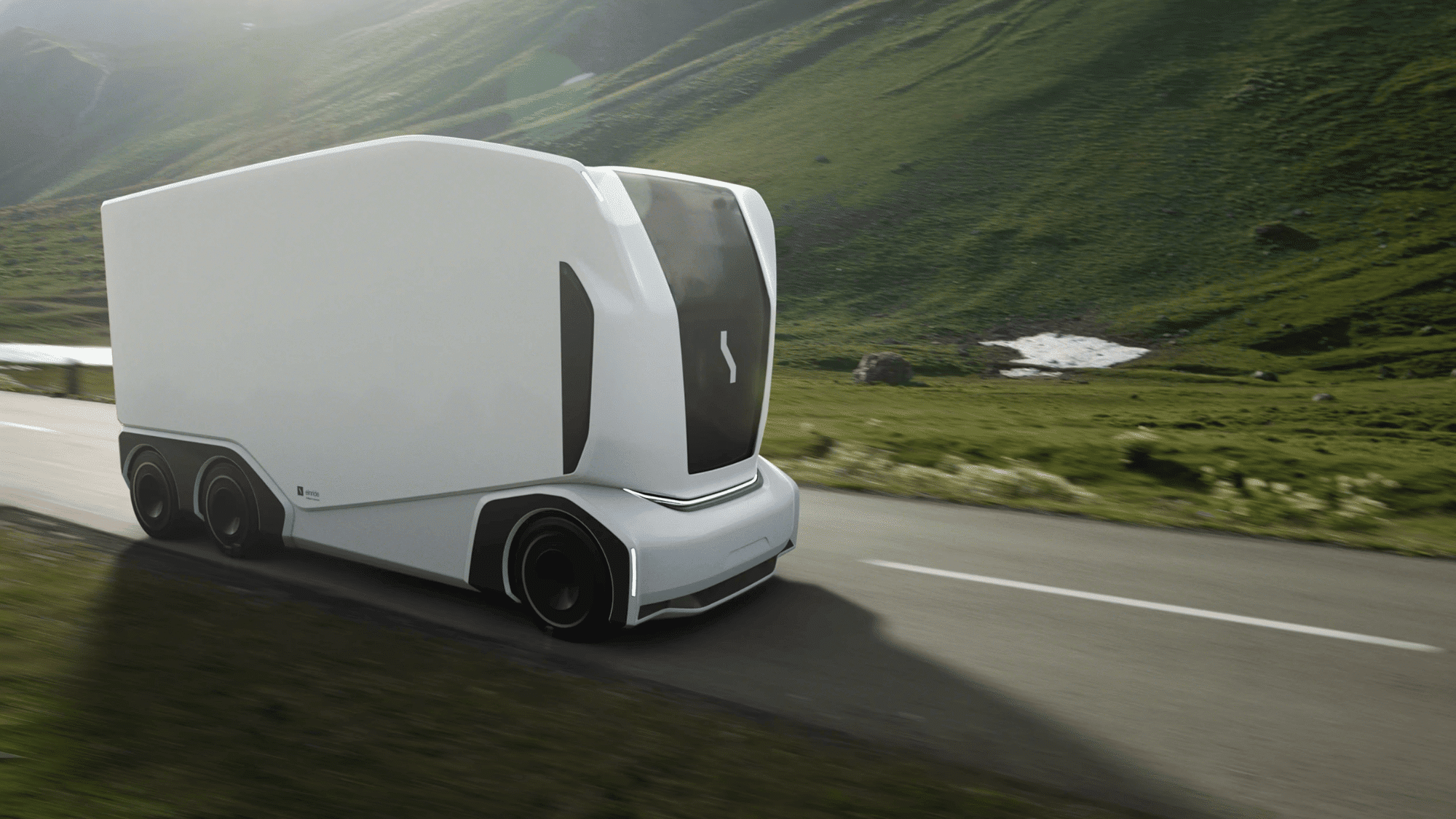

Einride, based in Sweden, takes a bold approach with electric freight pods that have no driver’s cabin at all. These pods are monitored remotely, blending sustainability with cutting-edge automation.
- Focused on zero-emission autonomous freight.
- Active in Europe and North America.
- Pioneering cableless, fully electric logistics.
Together, these companies are redefining how autonomous vehicles operate, turning futuristic concepts into everyday innovations that are steadily reshaping the way the world moves.
The Future of Self-Driving Cars
The future of self-driving cars, 2025 and beyond, looks promising but gradual.
According to McKinsey & Co., around 12% of new cars sold by 2030 will feature Level 3 or higher automation, signaling steady progress rather than an overnight transformation.
While the technology is advancing fast, mass adoption will take time as regulations, infrastructure, and consumer trust catch up.
Self-driving technology is expected to reshape several key areas of modern life:
- Public Transit: Autonomous buses and shuttles could provide safer, more efficient transportation in cities, reducing reliance on personal vehicles and cutting down traffic congestion.
- Freight Logistics: Automation in trucking and deliveries will lower costs, speed up operations, and make supply chains more resilient and reliable.
- City Planning: With fewer parking lots and smoother traffic flow, urban spaces can be redesigned for housing, parks, and pedestrian zones instead of vehicle storage.
While challenges remain, the road ahead for self-driving cars is filled with potential. Gradual integration, not sudden replacement, will define how automation reshapes mobility in the coming decade.
Wrapping It Up
After learning about both the pros and cons, I truly believe self-driving cars could change the way we live and travel.
They can make roads safer, help the environment, and make life easier for people who can’t drive, but they also bring real concerns about safety, jobs, and affordability.
I don’t think humans will stop driving anytime soon, but I do think technology will slowly take on a bigger role behind the wheel.
I’m excited to see how this technology grows in the coming years. If you enjoyed this breakdown, stick around. I’ll be sharing more simple, honest takes on the latest innovations shaping our future.

